Part 2: Cisco ASA/FTD Clustering Spanned EtherChannel Routed Mode
Part 2: Cisco ASA/FTD Clustering Spanned EtherChannel Routed Mode
In our example 2, we are going to talk about the ASA Clustering with Spanned EtherChannel Routed Mode which means that ASA cluster nodes at each of 2 data centers placed between the gateway router and an inside network at each site (East-West insertion).
⭐Related : Cisco Secure Firewall 7.x
⭐Related : Cisco Secure Firewall: Clustering Basics
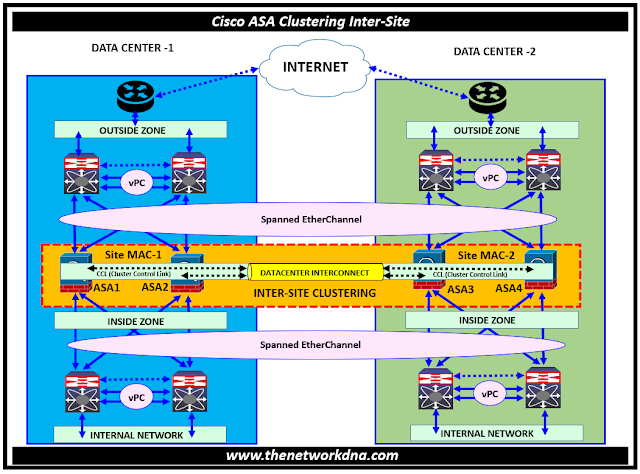
Fig 1.1- Cisco ASA/FTD Clustering Spanned EtherChannel Routed Mode
Over the DCI, the cluster control link connects the cluster nodes. To load balance traffic across cluster members, each data center's interior and outside routers use PBR, ECMP, and OSPF. Unless all ASA cluster nodes at a particular site fall down, traffic remains within each data center thanks to the assignment of a higher cost route across the DCI.
Each router sends traffic to the ASA cluster nodes at the other site via the DCI in the event that all of the cluster nodes at one site fail.
The cluster members at each site connect to the local switches using spanned EtherChannels for both the inside and outside networks. Each EtherChannel is spanned across all chassis in the cluster. Let's understand that
Data VLANs are extended between locations via VXLAN/OTV. You must implement filters that block the global MAC address to prevent traffic from passing through the DCI to the other site when it is intended for the cluster. If one site's cluster units become unavailable, you must remove the filters to allow traffic to be routed to the other site's cluster units.
Use VACLs to filter the global MAC address. Some switches, such as Nexus with the F3-series line card, require further ARP inspection to prevent ARP packets from reaching the global MAC address. To enable ARP inspection, you must configure both the site MAC address and the site IP address on the ASA.
The cluster serves as the gateway to the internal networks. The global virtual MAC, shared by all cluster units, is only utilized for packet reception. Outgoing packets are routed through a site-specific MAC address from each DC cluster. This feature stops the switches from learning the same global MAC address from both sites on different ports, preventing MAC flapping; instead, they only learn the site MAC address.
- All egress packets transmitted from the cluster utilize the site's MAC address and are localized at the data center.
- All ingress packets to the cluster are transmitted with the global MAC address, allowing them to be accepted by any of the units at either site; filters at the OTV localize traffic inside the datacenter.
⭐ Benefits of Spanned EtherChannel Routed Mode
- Load Balancing and Performance: Traffic is spread over all active interfaces in the EtherChannel, resulting in increased throughput.
- This redundancy helps to sustain performance even when individual links fail.
- Resilience and Failover: Spanned EtherChannel allows for faster failure detection than other methods.
- If a connection breaks, the remaining links in the channel will automatically handle the traffic, maintaining service continuity.
- Simplified Management: The EtherChannel is assigned a single IP address, which simplifies configuration and management when compared to handling individual interfaces.
- Compatibility: Spanned EtherChannel supports both routed and transparent firewall modes, providing implementation flexibility.
Continue Reading...
- Security: Cisco ASA Vs Cisco FTD - The Network DNA
- Site-to-Site VPN: IPSEC Tunnel Between an ASA and a Cisco IOS Router
- Cisco Security: Cisco ASA 5505 Interfaces configuration for Access Ports
- Cisco Security: Cisco ASA 5505 Interfaces configuration for Trunk Port
- Cisco ASA Series 1: Restoring the ASA to Factory Default Configuration
- Cisco ASA Series 2: Configuring NAT
- Cisco ASA Series 3: Easy VPN Remote
- Cisco ASA Series 4: Configuring VLANs and Sub interfaces
- Cisco ASA Series 5: Configuring Threat Detection
- Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel between Cisco ASA and Palo Alto Firewalls