Cisco Secure Firewall Modes
Cisco Secure Firewall Modes
Cisco Secure Firewalls deliver enhanced network protection against increasingly complex and evolving threats.
Cisco's security infrastructure is both flexible and integrated, enabling you to provide the strongest security posture possible for today and tomorrow.
Cisco enables you to extend your firewall solution to your existing network infrastructure, so you can deploy world-class security controls everywhere you need them, from your data center to your branch offices to your cloud environments.
There are two modes in which Cisco Secure Firewall works. These modes are :
- Routed Mode
- Transparent Mode
⭐Related : Cisco Next Generation Firewalls : Cisco Firepower 9300 Series introduction
⭐Related : Cisco Secure Firewall 7.x
⭐Related : Cisco Secure Firewall 7.x
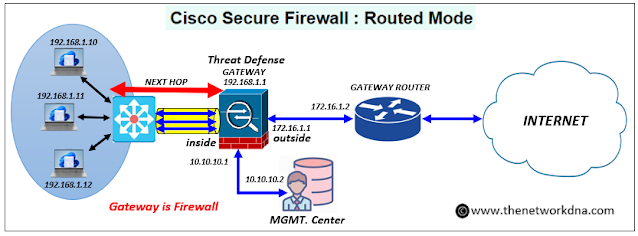
Cisco Secure Firewall : Routed Mode
Lets talk about the Cisco Secure Firewall Routed mode. Below are the functions are done by Cisco Secure Firewall in Routed mode.
- Default Gateway: The firewall can act as the default gateway for devices on the connected subnets.
- NGFW Capabilities : Along with the L3 routing, Firewall do its core functions like threat detection, intrusion prevention, and application control, filtering traffic based on your security policies.
- Layer 3 Operation: Cisco Secure Firewall acts as a layer 3 hop and Each interface can be connected to a different subnet. So you can route traffic between different subnets.
- Bridge Groups : Routed mode allows for using bridge groups. The firewall uses bridging techniques to pass traffic between them, and a Bridge Virtual Interface (BVI) with an IP address on the network handles routing between bridge groups and regular interfaces.
- Protocol Support : Routed mode supports static routing for manual configuration of routes and dynamic routing protocols like OSPF, RIP, or BGP for automatic route discovery and updates.
- Access Control: You can define firewall access rules on a per-interface basis, allowing you to control traffic flow between specific subnets and enforce security policies.
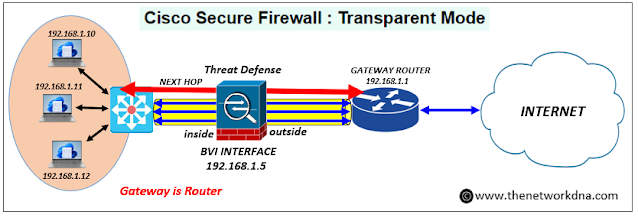
Cisco Secure Firewall : Transparent Mode
Lets talk about the Cisco Secure Firewall Transparent mode. Below are the functions are done by Cisco Secure Firewall in Routed mode.
- Layer 2 Operation: Transparent mode functions at Layer 2 (data link layer). This means it operates similarly to a switch, forwarding traffic based on MAC addresses without needing IP addresses assigned to each interface. So Firewall bridges the inside and outside interfaces into a single Layer 2 network and remains transparent to the hosts.
- No Routing: The firewall itself doesn't participate in IP routing. Devices on either side of the firewall see it as a bridge, and any routing between subnets is handled by existing routers in the network.
- Traffic Inspection: Even without IP routing, the firewall can still inspect all traffic passing through it, enforcing security policies and filtering out malicious content.
- Stateful Inspection (Optional): Transparent mode can optionally be configured for stateful inspection. This tracks connections and allows for more granular control over traffic flow based on established connections.
- Interfaces: Supports only two interfaces (inside and outside)
- Bridge Groups: Router needed to connect hosts within different bridge groups.
- No Default Gateway: No IPv4 address to interface and no default gateway for the hosts.
Cisco Secure Firewall : Routed Mode Vs. Transparent Mode
Here is a table comparing Cisco Secure Firewall Routed mode and Transparent mode:
Cisco Secure Firewall transparent mode is an excellent option for adding protection to a small network while minimal disruption.
If you require advanced routing capabilities, granular control over inter-subnet traffic, or detailed traffic analysis, routed mode is the preferable solution.
Continue Reading...
- Security: Cisco ASA Vs Cisco FTD - The Network DNA
- Site-to-Site VPN: IPSEC Tunnel Between an ASA and a Cisco IOS Router
- Cisco Security: Cisco ASA 5505 Interfaces configuration for Access Ports
- Cisco Security: Cisco ASA 5505 Interfaces configuration for Trunk Port
- Cisco ASA Series 1: Restoring the ASA to Factory Default Configuration
- Cisco ASA Series 2: Configuring NAT
- Cisco ASA Series 3: Easy VPN Remote
- Cisco ASA Series 4: Configuring VLANs and Sub interfaces
- Cisco ASA Series 5: Configuring Threat Detection
- Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel between Cisco ASA and Palo Alto Firewalls