In-Depth Comparison: Physical vs. Virtual Firewalls
In-Depth Comparison: Physical vs. Virtual Firewalls
There has never been a more pressing need for strong cybersecurity measures as the world grows more dependent on technology. As the first line of protection against hostile cyberattacks, firewalls are an essential part of every organization's cybersecurity strategy. But as technology has developed, the argument over virtual vs physical firewalls has gained a lot of momentum.
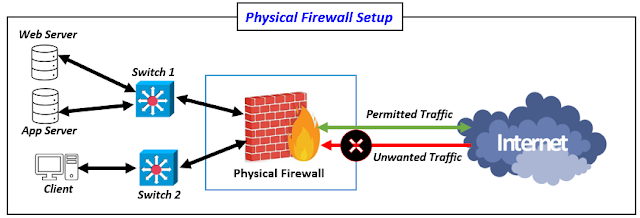
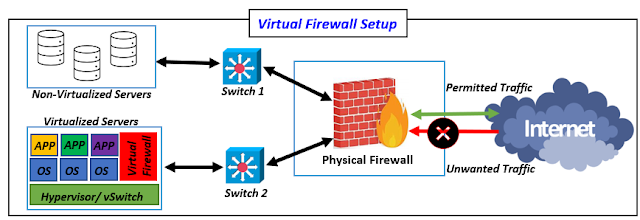
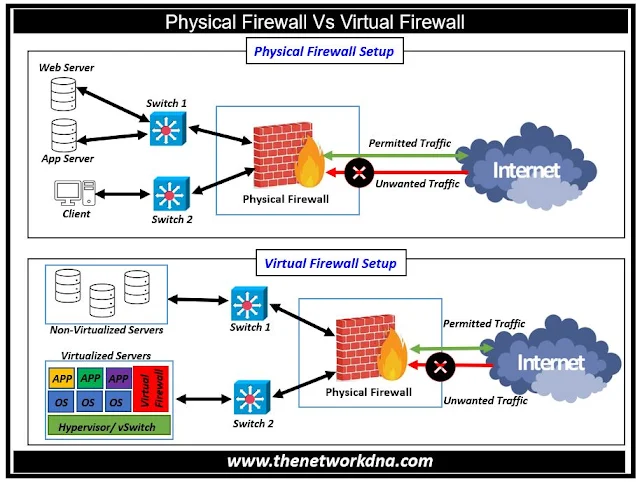 |
| Fig 1.1- Physical and Virtual Firewalls |
We are going to look at the features and comparisons between physical and virtual firewalls in this blog post, comparing the advantages and disadvantages of each to help you decide which is best for your company's cybersecurity requirements.
🚀🚀 Physical Firewalls 👇
A network's firewall plays a critical role in preventing malicious traffic from entering or leaving the network and protecting it from unauthorized access. By filtering incoming and outgoing traffic according to predefined security criteria, they operate as a barrier between a trusted internal network and an untrusted external network.
A physical firewall, sometimes referred to as a hardware firewall, is an independent device that is placed around a network's perimeter. It is a particular piece of equipment made especially with network security in mind. Multiple network interfaces are a common feature of physical firewalls, which enable them to separate various network segments and regulate traffic flow between them. Furthermore, a lot of physical firewalls have integrated security features like deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, and virtual private network (VPN) support, which provide all-around defense against a variety of online threats.
Physical firewalls have the major benefit of being able to handle large volumes of network traffic without affecting performance. They can process huge amounts of data since they are optimized for dedicated hardware, which makes them appropriate for enterprise-level networks with high traffic loads. Moreover, physical firewalls can frequently be set up for failover and high availability, providing ongoing security even in the case of hardware failures.
The lack of scalability and flexibility of physical firewalls is one of their main disadvantages. It can be difficult and time-consuming to add or change security rules on a physical firewall, particularly for businesses with dynamic network environments. Furthermore, purchasing and deploying hardware for physical firewalls typically requires a sizable upfront investment. The financial impact of building physical firewalls might be particularly high for smaller enterprises with limited resources.
🚀🚀 Features of Physical Firewalls 👇
- Controls the traffic that reaches servers intelligently.
- Specific rules must be set up for all traffic.
- Reduce the strain on server resources.
- A single hardware firewall protects all systems connected to the server and avoids the need to install software on each machine.
- Updating protection settings guarantees that all devices are secure against vulnerabilities.
- Physical firewalls provide better security since they have their own operating system and are less vulnerable to threats that software firewalls face when the system is corrupted.
🚀🚀 Virtual Firewalls 👇
Virtual firewalls are software-based solutions that can be used in virtualized settings, on cloud platforms, or as standalone software programs. Virtual firewalls provide the same basic functions as physical firewalls, such as packet filtering, network address translation, and VPN compatibility, but with greater flexibility and scalability. They are simple to provision and configure to meet the changing needs of a dynamic network, enabling for seamless adaptation to changing security requirements.
The ability of virtual firewalls to connect with virtualization platforms and cloud services to provide security for virtual machines and cloud workloads. Because they can provide the same level of protection across virtual and physical infrastructure, they are an excellent solution for enterprises embracing cloud computing and hybrid IT systems. Furthermore, virtual firewalls frequently provide centralized management capabilities that enable unified security rules and easier administration across remote settings.
The advantage of virtual firewalls is their low cost and resource efficiency. Virtual firewalls, because they are software-based, eliminate the need for dedicated hardware and physical maintenance, lowering the upfront expenses involved with hardware procurement and installation. They also provide the ability to scale up or down dependent on demand, making them a more cost-effective option for enterprises with fluctuating network needs.
While virtual firewalls have various advantages, they also have certain drawbacks. One of the most significant issues with virtual firewalls is their reliance on the underlying virtual or cloud architecture. The performance and security of the underlying hypervisor or cloud platform can have an impact on the effectiveness of a virtual firewall in a shared virtualized environment. This adds a layer of dependency, which may raise issues about the virtual firewall's overall robustness and isolation.
🚀🚀 Features of Virtual Firewalls 👇
- Data security for all
- To secure virtual data centers, manage, monitor, and filter all traffic.
- Advanced access policies help to secure remote access networks.
- Maintain application integrity and confidentiality.
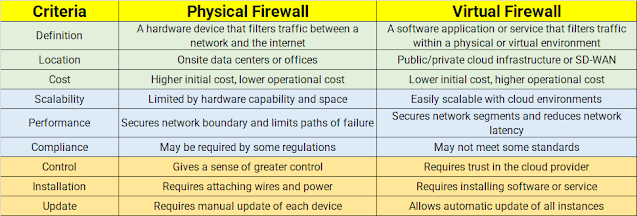
🚀🚀 Physical Vs Virtual Firewalls 👇
⭐ Related : Network Based Firewall Vs Host Based Firewall
- Security: Cisco ASA Vs Cisco FTD - The Network DNA
- Site-to-Site VPN: IPSEC Tunnel Between an ASA and a Cisco IOS Router
- Cisco Security: Cisco ASA 5505 Interfaces configuration for Access Ports
- Cisco Security: Cisco ASA 5505 Interfaces configuration for Trunk Port
- Cisco ASA Series 1: Restoring the ASA to Factory Default Configuration
- Cisco ASA Series 2: Configuring NAT
- Cisco ASA Series 3: Easy VPN Remote
- Cisco ASA Series 4: Configuring VLANs and Sub interfaces
- Cisco ASA Series 5: Configuring Threat Detection
- Site to Site IPSec VPN Tunnel between Cisco ASA and Palo Alto Firewalls