OSPF External Routes: N1 & N2 Routes
OSPF External Routes: N1 & N2 Routes
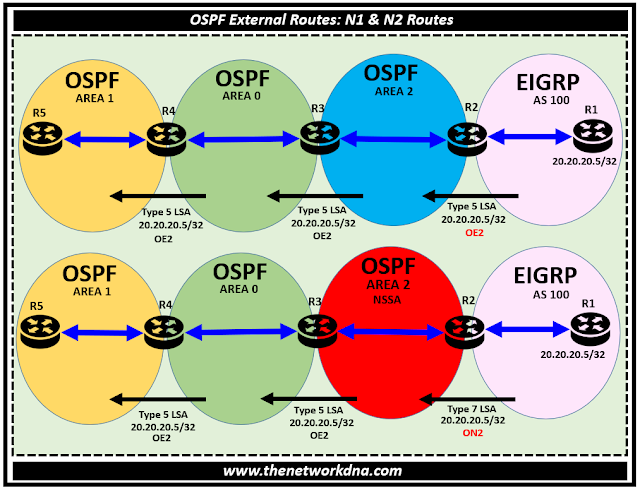
Generally if an OSPF area is connected to the external, it receives OE2 routes as external routes on ASBR router. OE2 (External Type 2) routes maintain the original cost they had in the other routing protocol or static configuration. OSPF doesn't modify the cost during advertisement.
But if the OSPF area which is a NSSA area and connected to External and LSA type 5 is not allowed which means OE2 is not allowed in that area, so how can NSSA area and other areas beyond it learn about the external routes ?
⭐Related : OSPF External Routes: E1 Vs E2 Routes
Here comes the ON2 routes which is an NSSA Type 2 and is similar to E2, N2 routes retain the original cost from the external source. No additional cost is added within the NSSA area.
Lets check the scenario here to understand more in depth, you will see two images where top one shows in case of normal area and below one is the NSSA area, you will see the type of routes injected into the OSPF areas.
⭐Related : Top OSPF Protocol Interview Questions and Answers
⭐Related : OSPF protocol : OSPF Packet Types
 |
| Fig 1.1- OSPF External Routes: N1 & N2 Routes |
So in case of NSSA area, Router R2 received external routes as a ON2 route and pushed that to the Area 2 which is a NSSA area, once it reaches to Router R3 ( ABR) it converts back to OE2 external route and pushed to area 0 and further.
As many of you aware that Not-So-Stubby Areas (NSSA) are a special type of OSPF area designed to simplify routing and prevent routing loops. They achieve this by suppressing the advertisement of certain Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) within the area.
So now you understand that the ON1 and ON2 routes are specific to NSSA areas and function similarly to OE1 and OE2 routes
⭐Related : Introduction to OSPF LSA Types
⭐Related : Introduction to OSPF Area Types
Check what routes you are receiving on router R2
Continue Reading...
- OSPF Show Commands on Cisco, Juniper, Huawei, HP and Arista Networks devices
- How to Optimize Your MPLS VPN with OSPF Sham-Link
- OSPF protocol : OSPF Packet Types
- OSPF NSSA Area introduction and Configuration
- Facts about DR and BDR selection in OSPF
- OSPF and BGP configuration setup on a vEdge Router
- OSPF Configuration Guide : OSPF Distance External Command Behavior
- A quick difference: OSPF Vs IS-IS Dynamic Routing Protocol
- Routing: Configuration OSPF To Filter Type-5 LSAs
- Introduction to OSPFv3 AS External LSA Route Calculation
- Differences between OSPFv3 and OSPFv2
- OSPF Over non-Broadcast Networks ( NBMA) basics and Configuration
- OSPF Configurations in Huawei Routers
- Quick tips to OSPF Routing Protocol for Network Engineers
- OSPF Basic configuration Step by step on Cisco Routers
- OSPF Basics : Simple points to study
- OSPF prefix-suppression- Configurations and Verification
- OSPF LSA-ID Conflict : %OSPF-4-CONFLICTING_LSAID
- Cisco IOS-XE: OSPF stuck in INIT - LLS TLV
- Configure Redistribution of iBGP Routes Into OSPF
- Cisco and Juniper Routers : OSPF point to multipoint configurations







