Cisco SDWAN: Cloud OnRamp for SaaS DNS Workflow
Cisco SDWAN: Cloud OnRamp for SaaS DNS Workflow
Before we discuss the Cisco SDWAN Cloud OnRamp SaaS DNS Workflow, let's briefly touch on what Cisco cloud onRamp for SaaS actually is.
What is Cisco cloud onRamp for SaaS?
A smooth end-user experience is offered by Cloud OnRamp for SaaS, an automated solution, for popular corporate applications including Webex, Microsoft 365, Salesforce, Google apps, AWS, Oracle, Box, and more.
You may do this to allow Cisco SDWAN to choose the optimal path for each SaaS application using the chosen interfaces. It also allows you to choose individual SaaS apps and interfaces.
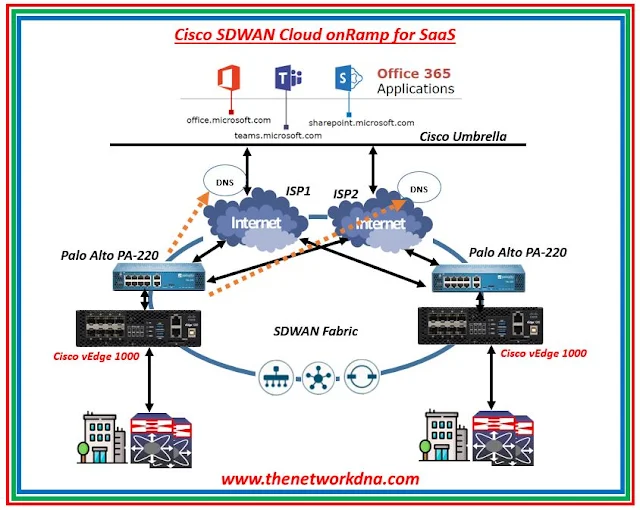 |
| Fig 1.1- Cisco SDWAN: Cloud OnRamp for SaaS DNS Workflow |
You must first enable the Cloud onRamp for SaaS capability globally. The SaaS apps that will be utilized and kept an eye on are then outlined. The DIA, gateway, and client sites will then all be operational.
By sending probes to all possible paths to SaaS applications, Cisco SDWAN Cloud OnRamp for SaaS continuously monitors all possible paths, and then, based on probe latency and loss, selects the best path for routing the traffic, ensuring fast, reliable, and efficient connectivity.
Check out the below article to see step by step procedure to enable Cloud onRamp for SaaS.
Cisco SDWAN : Enable onRamp on vManage - The Network DNA
Quality-of-Experience (QoE) scores are calculated using probe loss and latency values in Cisco vManage, Cisco SDWAN's management plane, which provides network administrators with insight into network path performance over time, allowing them to troubleshoot and improve the user experience.
Cloud OnRamp for SaaS Workflow
To guarantee that the optimum performance channel is used for user traffic, Cloud OnRamp for SaaS uses an Cisco SDWAN router as a DNS proxy for SaaS traffic.
Step 1: Host performs DNS resolution for SaaS app
Step 2: User DNS request is intercepted by the WAN Edge router DPI engine. Non-SaaS applications follow the standard routing path, whereas SaaS application traffic is subsequently directed to the DNS server indicated in VPN0, which is known to have the highest performance.
Step 3: The DNS request is sent via the highest performing DIA circuit after the WAN Edge overwrites the DNS request's destination address.
Step 4: Upon getting a DNS answer, WAN Edge replaces the destination address with the IP address of the client.






