Full Tunnel vs Split Tunnel VPN
Full Tunnel vs Split Tunnel VPN
Virtual private networks, or VPNs, are becoming increasingly important for businesses who has remote workers. Through the creation of an encrypted tunnel for internet traffic, VPNs improve privacy, security, and access to resources that are banned. The purpose is to sending all traffic via a VPN tunnel.
Fig 1.1- Full Tunnel vs Split Tunnel VPN
When accessing Wi-Fi at a public place internet, customers may browse the internet safely with the help of a VPN service like Cisco AnyConnect (Corporates VPN) or Express VPN (Individual users).
Instead of utilizing the public Wi-Fi, which is vulnerable to hacking if it is not encrypted or has inadequate security, users can establish a virtual private network (VPN).
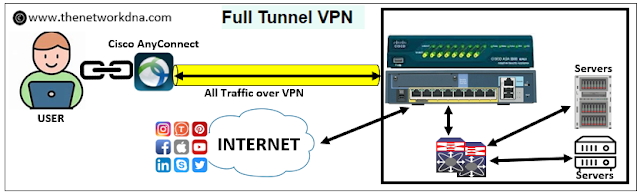
1. Full Tunnel VPN
A full tunnel virtual private network (VPN), also called a traditional VPN, encrypts and passes all of your internet data via a secure tunnel.
This implies that an additional layer of security is applied to everything you do online, including sending emails, viewing websites, and streaming media.
- Enhanced security: When utilizing public Wi-Fi networks, a full tunnel VPN offers the strongest protection from all kinds of online threats because it encrypts all of your traffic.
- Privacy: It is more difficult to track your browsing activities and personal information when your online activity is hidden from your internet service provider (ISP), outsiders, and any hackers.
- Location spoofing: this approach makes your internet traffic seem to be coming from the location of the VPN server, which may help you get around censorship or access content that is geo blocked.
Where there are specific organization policies to route all the traffic over the VPN and the internet traffic must exit from the Datacenter, they use full tunnel VPN.
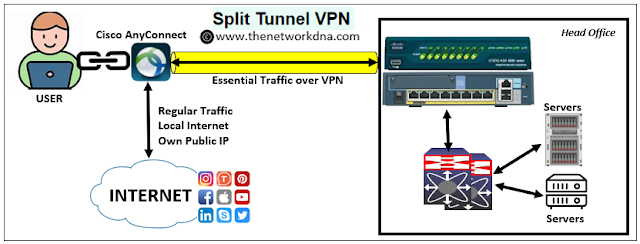
2. Split Tunnel VPN
When a VPN is used to route only certain types of data traffic. The remaining data is forward straight via the local internet at the same moment is called Split tunnel VPN.
Split tunneling allows some data and apps to connect directly to the Internet, while other data and apps are routed via a secure virtual private network (VPN). This is especially important for VPNs that offer remote access when your computer is directly connected to a remote network at your workplace, like in a work-from-home scenario.
Split tunneling allows you to use both the public internet and the VPN tunnel, as opposed to just one. Sensitive traffic, including corporate networks, financial apps, medical systems, and streaming media that requires location spoofing, is routed through a secure VPN connection.
Routine internet activities like gaming, video streaming, and simple site browsing continue to take place outside on public networks in the time between.
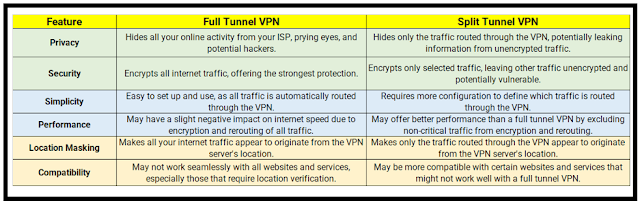
3. Full Tunnel VPN Vs. Split Tunnel VPN
When talking about both, below is the table shows the comparison between Full Tunnel VPN and Split Tunnel VPN.
Split-tunnel VPNs are ideal for most home users since they allow you to transport traffic over the VPN only when necessary. Sometimes it is ideal for business customers to route all traffic through the VPN tunnel because it offers benefits in terms of security.
Continue Reading...
- Back to Basics: Understand the different types of VPN
- Palo Alto Networks : Policy based VPN vs Route based VPN
- Quick start on Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN
- Protecting Your Data: How the Top 5 VPN Services for 2024 Ensure Online Security
- Cisco Meraki to Azure Site to Site VPN
- Understanding the Basics: L2VPN vs L3VPN
- Security: FortiGate to SonicWall VPN Tunnel setup