Basics of SD-Access with Cisco Catalyst Center
Basics of SD-Access with Cisco Catalyst Center
SD-Access is an evolution of the traditional manual approach of design and deployment of the network components in the Campus network with the help of a controller-based system with simple business intent inputs. It adds flexibility, scalability, and efficiency, which is automated and quickly meets the business’s requirements.
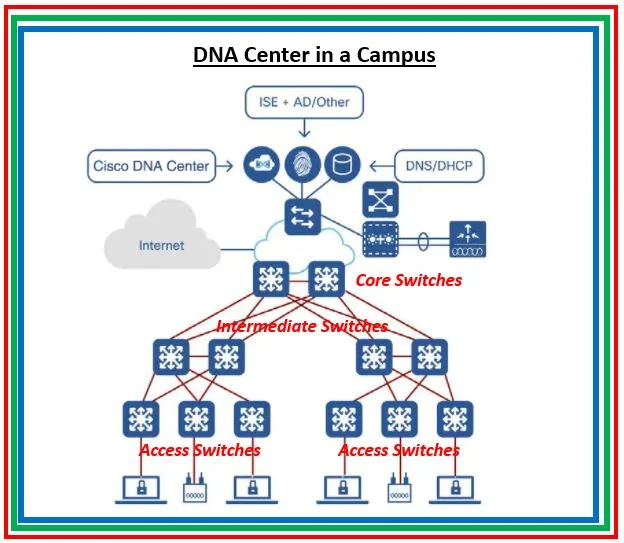 |
| Fig 1.1- Cisco DNA Center |
Catalyst Center (Earlier DNA Center) host the SD-Access application. It is right to say SD-Access is one of the capabilities of DNA Center.
Catalyst Center (Earlier DNA Center) is the centralized controller to take care of the complete life-cycle of network devices starting from Day 0 (Onboarding/provisioning), Day 1 (deployment of the device), Day 2 (Monitoring & troubleshooting device), and day n (optimize the performance). Network performance, network insight, and device telemetry are available using the Assurance and Analytics application of DNA Center.
Note ⭐: Cisco Catalyst Center is a new name to Cisco DNA Center
SD-Access Fabric Roles
Control Plane Node : A Control Plane Node in Cisco SD-Access is a device that provides functions of LISP Map server and Map resolver. It registers all the EID (Endpoint Identifier) that are connected to fabric Edge node and maps them to RLOC (Routing Locator). It can also be configured on the same fabric node as a border node
Border Node: A Border Node in Cisco SD-Access is a device that serves as the gateway between the fabric and external networks. It can be configured as Internal only, External only, or Internal and External depending on the connectivity needs. It can also be part of a transit network that connects different fabric sites.
Edge Node: An Edge Node in Cisco SD-Access is a device that replaces the access layer switch in a traditional campus LAN design. It provides first-hop services for users and devices connected to the fabric and registers them with the Control Plane Node. It implements a Layer 3 routed access design and uses LISP xTR functionality
Intermediate Node: An Intermediate Node in Cisco SD-Access is a device that is part of the Layer 3 network (underlay) that connects the border nodes and edge nodes. It provides IP reachability between the devices that operate in a fabric function.
Extended Node: An Extended Node in Cisco SD-Access is a device that extends the fabric overlay and segmentation to non-fabric devices. It can be either a Policy Extended Node (PEN) or a regular Extended Node (EN) depending on the device type and the configuration
Fabric WLC: A Fabric WLC in Cisco SD-Access is a wireless controller that is fabric enabled and participates in the SDA control plane. It connects wireless endpoints and APs to the SD-Access fabric via an internal border node. It provides onboarding and mobility features for wireless users and endpoints
Fabric-Mode Access Point: A Fabric-Mode Access Point in Cisco SD-Access is an access point that is fabric enabled and configured with one or more fabric-enabled SSIDs. It encapsulates wireless traffic with VXLAN at the AP and sends it to the fabric through an edge node. It is recognized by the edge node as a unique wired host and assigned to a separate overlay network called INFRA VN
SD-Access Embedded Wireless: SD-Access Embedded Wireless is a feature that enables wireless controller functionality on Catalyst 9000 Series switches without a hardware WLC. It is a software package that runs in Install mode and integrates wireless access into the SD-Access fabric. It is suitable for distributed branches and small campuses
Transit and Peer Networks: Transit and Peer Networks in Cisco SD-Access are networks that connect multiple fabric sites together or between a fabric site and the external world. They are configured on the border nodes of the fabric sites. There are two types of transit networks: SD-Access transit and IP-based transit. SD-Access transit uses a native SD-Access fabric with a domain-wide control plane node, while IP-based transit uses a traditional IP-based network with VRF and SGT remapping
Transit Control Plane Node: A Transit Control Plane Node in Cisco SD-Access is a fabric role construct that operates as a domain-wide control plane node for inter-site communication. It is only required when using SD-Access transits. It is part of the underlay network and needs to have reachability to the border nodes and Cisco DNA Center. It helps to exchange LISP mapping information between fabric sites
Fabric Domain : A Fabric Domain in Cisco SD-Access is a hierarchical representation of fabric sites managed by Cisco DNA Center. A fabric domain can consist of multiple fabric sites and each site has its own devices that provide scale, resiliency and survivability. A fabric site is a logical grouping of devices that share the same control plane, data plane and policy plane. A fabric site can have different roles such as edge, border, control plane and transit
Fabric Site : A Fabric Site in Cisco SD-Access is a logical grouping of devices that share the same control plane, data plane and policy plane. A fabric site is autonomous from other fabric sites from the connectivity perspective. A fabric site can have different roles such as edge, border, control plane and transit. A fabric site is managed by Cisco DNA Center.
Fabric in a Box: Fabric in a Box is an SD-Access construct where the border node, control plane node, and edge node are running on the same fabric node. This may be a single switch, a switch with hardware stacking, or a StackWise Virtual deployment. The Fabric in a Box Site Reference Model should target less than 200 endpoints.
Continue Reading...
- Updates in Cisco DNA Center 2.3.5.0 - The Network DNA
- Updates in Cisco DNA Center 2.3.4.x - The Network DNA
- Virtual Appliance Cisco DNA Center on Amazon AWS - The Network DNA
- Cisco DNA Center Guardian Version 2.3.3.x - Host entry cleanup in Maglev
- Part 2: How to run CBAR on Cisco DNA center - The Network DNA
- Cisco DNA Center : RMA Workflow - The Network DNA
- Cisco DNA Center : Gen 2 DNA Center Appliances - The Network DNA
- Cisco DNA Center : Setting up 3 node cluster controllers - The Network DNA
- Updates in Cisco DNA Center 2.2.3.3 - The Network DNA







