Offensive vs. Defensive Security: Which Strategy is Right for You?
Offensive vs. Defensive Security: Which Strategy is Right for You?
Offensive security is the proactive method of detecting and exploiting vulnerabilities and flaws in systems and networks before hostile actors may exploit them. Offensive security specialists replicate real-world assaults and assess an organization's security posture using tools and techniques such as penetration testing, ethical hacking, vulnerability scanning, and red teaming. Offensive security aims to detect and report security flaws, as well as make recommendations for improvement. To delve into the dynamic field of offensive security and sharpen your skills in detecting and countering vulnerabilities, Lumify Work provides specialized courses offering hands-on experience with penetration testing, ethical hacking, vulnerability scanning, and red teaming techniques
By putting security controls and procedures in place, defensive security takes a reactive approach to avoiding and minimizing cyberattacks. To monitor, identify, and react to cyber threats, defensive security experts utilize technologies and procedures include firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, backup, incident response, and blue teaming. Protecting the availability, integrity, and confidentiality of data and systems is the aim of defensive security.
Although the concepts of offensive and defensive security may appear to be at odds, they work best together. Both offensive testing to identify vulnerabilities and defensive measures to guard against exploitation are components of a well-rounded cybersecurity strategy. Discovering vulnerabilities during the offensive phase helps organizations strengthen their defenses during the defensive phase.
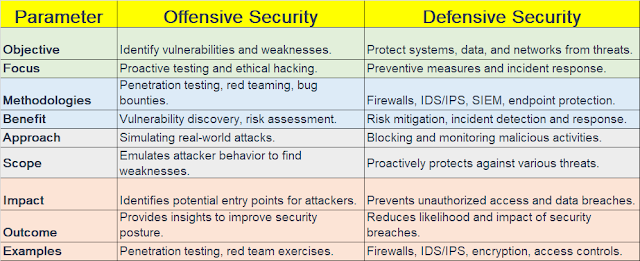 |
| Fig 1.1- Offensive vs. Defensive Security |
Organizations must be protected from cyber attacks using both offensive and defensive security measures. They cooperate to create a well-rounded and successful security plan since they are complementary to one another. Some examples of cyber stories from the field that illustrate the importance of both approaches are:
- A significant data breach that affected Equifax in 2017 resulted in the exposure of 147 million people's personal data. Because Equifax neglected to patch a known vulnerability in Apache Struts, the intrusion occurred. This demonstrates the necessity for offensive security to find and fix vulnerabilities before hackers can take advantage of them.
- A data breach affecting 500 million guests of Marriott's Starwood hotel network was made public in 2018. A vulnerable database that had been accessible by hackers since 2014 was what led to the breach. This demonstrates the necessity of defensive security to keep an eye out for unauthorized access and act fast to limit the harm.
- A data breach affecting 106 million customers in the US and Canada was reported by Capital One in 2019. A poorly constructed firewall allowed an attacker to access a cloud server that housed client data, which led to the breach. The attacker was a former worker of Capital One's cloud supplier, Amazon Web Services (AWS). This demonstrates the necessity for both offensive and defensive security to test, protect, and guard against insider threats in cloud systems.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the mutually beneficial interaction between offensive and defensive security emphasizes how diverse cybersecurity is. While preventative measures defend against possible attacks, ethical hacking helps fortify defenses. The interaction of these two approaches builds a strong ecosystem to defend digital assets and keep enemies at bay in the dynamic field of cybersecurity.







