Keeping Your Network Secure and Dependable
FortiGate Firewall High Availability
In today's fast-paced business world, enhanced dependability and higher performance are essential criteria for any networking component. That's why FortiGate High Availability (HA) is the perfect solution for your business.
Implementing FortiGate HA is easy - simply set up a cluster of two or more FortiGate devices. The cluster works together to process network traffic and offer standard security services like firewalling, VPN, IPS, virus scanning, web filtering, and spam filtering. And the best part? The HA cluster appears to the network as one FortiGate device, ensuring seamless operation and maximum uptime.
- The individual FortiGate devices in the cluster are called cluster units.
- These cluster units exchange configuration and status data, ensuring that the cluster is always up-to-date.
- If one unit in the cluster malfunctions, the other units immediately take over its tasks without any interruption.
- The cluster is managed by one primary unit, also known as the master unit, and one or more inferior units, also known as slave or backup units.
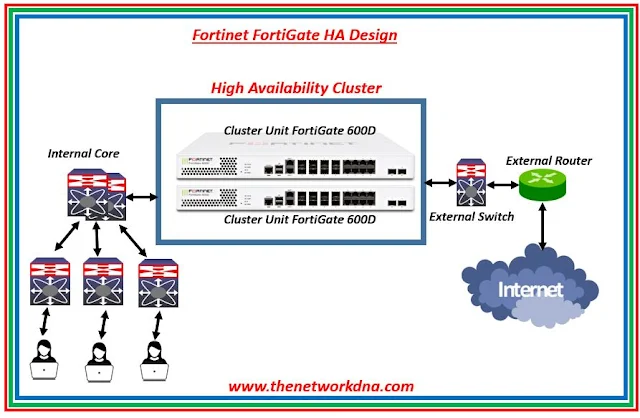 |
| Fig 1.1- Fortinet FortiGate HA Design |
With FortiGate HA, your network is never dependent on a single device. If one unit fails, the other units in the cluster will take over, ensuring that your network remains secure and operational.Performance may be improved by using load balancing, a second HA function. By splitting the workload of handling network traffic processing and security services, a cluster of FortiGate devices can improve overall network performance. The cluster adds improved speed without modifying your network's configuration since it appears to your network as a single device.
For a FortiGate running virtual domains, virtual clustering extends HA functionality to offer failover protection and load balancing. A cluster of two FortiGate units running in virtual domains makes up a virtual cluster. The cluster units may load balance traffic from many virtual domains.
FortiGate HA comes in two modes: Active-Passive and Active-Active.
Active-passive HA (failover protection)
Protection from hot standby failover is provided by an active-passive (A-P) HA cluster.
A primary unit that processes traffic made up of communication sessions and one or more subordinate units make up an active-passive cluster. Although they are linked to the network and the main unit, the subordinate units do not handle communication sessions.
The subordinate units operate in a standby mode instead. The configuration of the subordinate units is synchronized with the configuration of the major unit during this standby state, and they also keep track of the primary unit's condition.
Subordinate units get cluster status information from the primary unit if session failover is enabled. Lists of all communication sessions that the primary unit is processing are included in the cluster status information. If the primary unit fails, the subordinate units utilize this information to resume processing network communications sessions.
Device failover among cluster units is transparent thanks to active-passive HA. A new cluster unit is added right away if one fails. Additionally, seamless connection failover between cluster units is provided via active-passive HA. The link state database is updated when a cluster unit interface fails or becomes disconnected, and the cluster may choose to negotiate for a new main unit.
Active-passive HA offers session failover for the majority of TCP, UDP, ICMP, multicast, and broadcast communication sessions if session failover is enabled. For communication sessions that firewall policies that contain protection profiles approve, active-passive HA does not offer session failover. Compared to active-active HA, active-passive HA offers a more robust environment for session failover. TCP sessions are the only ones that can fail over with active-active HA.
Active-Active HA (load balancing and failover protection)
All cluster units' communication sessions are load balanced among them using active-active (A-A) HA. A main unit that handles communication sessions is part of an active-active HA cluster, along with one or more secondary units that do the same. All sessions are received by the primary unit, which then distributes sessions for firewall rules with protection profiles to every cluster unit. Load balancing protection profile traffic may lead an active-active cluster to have higher throughput than an active-passive cluster or a solitary FortiGate device since processing protection profile sessions can be CPU and memory-intensive.
Additionally, you may activate the load-balance-all CLI term to force the primary unit to load balance both protection profile sessions and all TCP connections. Load balancing protection profile sessions is more likely to increase throughput than load balancing TCP sessions. So, load-balance-all is by default turned off.
When active-active HA load balancing is in operation, the primary unit uses the configured load balancing schedule to determine which cluster unit will process the session when it receives the first packet of a protection profile session (or a TCP session if load-balance-all is enabled). The cluster load balancing session database in the primary unit contains the load balancing data for each active load balanced session. The primary unit may then route all of the remaining packets in each session to the proper cluster unit using the data in this table. All cluster units are in sync with regard to the load balancing session table.
Sessions for UDP, ICMP, multicast, and broadcast are always handled by the primary unit and are never load balanced. Sessions for VoIP, instant messaging, IPSec VPN, HTTPS, and SSL VPN are likewise always handled only by the primary unit.
Similar to active-passive HA, active-active HA offers device and link failover protection in addition to load balancing. A secondary unit takes over as the primary unit and continues to run the cluster if the first unit fails.
All TCP sessions, with the exception of protection profile sessions, are protected against session failover by active-active HA. For protection profile sessions, active-active HA does not offer session failover. Additionally, UDP, ICMP, multicast, and broadcast session failover is not supported by active-active HA. All UDP, ICMP, multicast, and broadcast sessions as well as protection profile sessions are not failed over and must be resumed.
The primary unit redistributes all TCP communications sessions across the remaining cluster units in the event that a subordinate unit fails. Sessions for protection profile that are already running on the failed subordinate unit are not failed over and must be resumed. The primary unit's processing of all sessions, including UDP, ICMP, multicast, and broadcast sessions, is unaffected.
Active-active HA can be a less reliable session failover solution than active-passive HA since it does not handle failover of UDP, ICMP, multicast, and broadcast sessions.
By processing the protection profile sessions that were being handled by the cluster units that are still operational, active-active HA keeps as many protection profile sessions as it can after a failover.
Continue Reading...
More on Fortinet..








