Part 1: VRF-Aware IPsec Overview
Part 1: VRF-Aware IPsec Overview
VRF-Aware IPsec is a feature that allows you to map IP Security (IPsec) tunnel & connect multiple Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to a single router using IPsec encryption, all while keeping the traffic for each VPN separate.
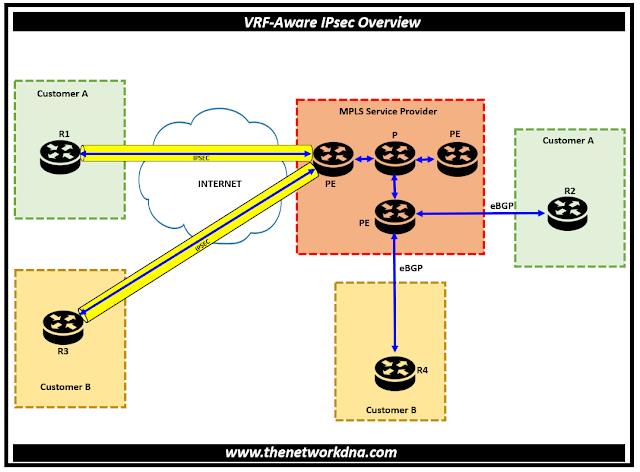
Every IPsec tunnel has two VRF domains connected to it. The inside, protected IP packet is part of a different domain known as the IVRF, while the outer encapsulated packet is part of one VRF domain that we will refer to as the FVRF. To put it another way, the source and destination addresses of the inner packet belong to the IVRF, whereas the local endpoint of the IPsec tunnel is part of the FVRF.
A single interface can serve as the endpoint of one or more IPsec tunnels. All of these tunnels have the same FVRF, which is set to the VRF that is set up on that interface. Depending on the VRF specified in the Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) profile that is linked to a crypto map entry, the IVRF of these tunnels may vary.
Fig 1.1- VRF-Aware IPsec Overview ( IPSEC + MPLS)
⭐ Terminology
VRF : VRF stands for Virtual Routing Forwarding and is a separate routing table within a router. VRFs are to a router what VLANs are to a switch. Using VRFs, it is possible to virtualize a single router into several instances, each of them being (relatively) independent of each other, allowing for overlapping subnets, separate instances of routing protocols, separate set of interfaces assigned to each VRF.
⭐Related : Introduction to VRF(Virtual Routing forwarding)
⭐Related : Do you know about VRF lite in MPLS networks ?
Global VRF : The routing instance that is used if no specific VRF is defined. If there is no VRF instance configured on interface, that interface belongs to global VRF.
Inside VRF (IVRF) : Inside VRF contains the clear-text traffic (before encryption for outbound flows and after decryption for inbound flows). Typically, Each customer link has its own VRF instance configured on PE Routers, exchanged routing via MP-BGP and route traffic over MPLS network.
Front Door VRF (FVRF) : Front-door VRF (or outside VRF), the VRF that contain the encrypted traffic. Typically, this VRF is used for internet traffic and VPN endpoint IP addresses are part of this VRF.
⭐ Packet Flow into the IPsec Tunnel
- A VPN packet arrives from the Service Provider MPLS backbone network to the PE and is routed through an interface facing the Internet.
- The packet is matched against the Security Policy Database (SPD), and the packet is IPsec encapsulated. The SPD includes the IVRF and the access control list (ACL).
- The IPsec encapsulated packet is then forwarded using the FVRF routing table.
⭐ Packet Flow from the IPsec Tunnel
- An IPsec-encapsulated packet arrives at the PE router from the remote IPsec endpoint.
- IPsec performs the Security Association (SA) lookup for the Security Parameter Index (SPI), destination, and protocol.
- The packet is decapsulated using the SA and is associated with IVRF.
- The packet is further forwarded using the IVRF routing table.
Continue Reading...