The Evolution: Exploring the Origins of SD-WAN discussions
The Evolution: Exploring the Origins of SD-WAN discussions
A virtualized network overlay called a software-defined wide-area network (SD-WAN) enables businesses to grow and remotely operate their networks over vast geographic areas with ease. Large retail chain stores or other sites can have several branch locations connected to a central head office via an SD-WAN. Compared to a standard WAN design, this one is more accessible and adaptable since it is isolated from hardware.
⭐Related : The Network DNA : Viptela SDWAN
⭐Related : The Network DNA : Silver-Peak SDWAN
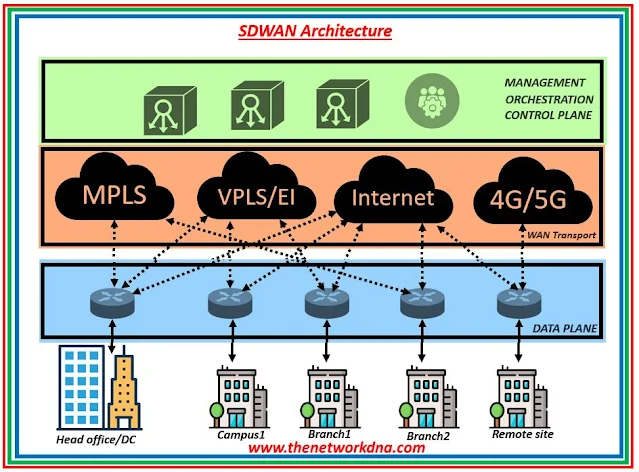 |
| Fig 1.1- SDWAN Architecture |
⚡ SDWAN Advantages 🔥🔥
- Using dynamic load balancing to boost bandwidth by fully using inactive backup connections
- By allowing direct internet connectivity at the branch, cloud-native apps can offer a better user experience.
- Lowering deployment and administration expenses by using cloud-based centralized management and zero touch provisioning
- Reducing WAN expenses by substituting less costly internet or LTE connection for MPLS
⚡ SDWAN Components ✴✴
- An enterprise can access a carrier network over the SD-WAN edge.
- IT experts can evaluate traffic and set policies with a single pane of glass thanks to the virtualized network manager called SD-WAN Orchestrator.
- For all SD-WAN Edges connected to it, the SD-WAN Controller offers virtual or physical device administration.
⚡ SD-WAN Architecture 💥💥
- SD-WAN on-site: When SD-WAN boxes are installed at a customer's location, they connect to other locations and carry out real-time traffic shaping at each one.
- SDWANs with cloud: When an SD-WAN architecture is cloud-enabled, the performance of cloud-native apps is improved overall because the on-site SD-WAN box is connected to a virtual cloud gateway over the internet.
- Backbone SD-WAN-Enabled and Cloud-Capable: Using a nearby point of presence (PoP) to link the network and divert traffic into the provider's backbone, this method gives organizations an additional backup. Reduced latency, packet loss, and jitter is guaranteed for those real-time and latency-sensitive workloads with this additional link.
⚡ SD-WAN Deployment scenario 🌐🌐
- SD-WAN solution delivered via several ISPs : ISPs can provide broadband services via DSL or Cable Internet, Dedicated Internet Access, or a combination of the three. By activating idle backup circuits, SD-WAN enables WAN redundancy and increases bandwidth.
- DIA for Cloud Apps: The SD-WAN solution delivers direct Internet access (DIA) and application visibility; branch connectivity to the cloud does not require a trip to headquarters, reducing backhaul and improving user experience on cloud-native apps. Furthermore, application steering on SD-WAN enables business vital applications to cross MPLS with reduced latency, packet loss, and jitter; none critical applications traverse IPsec VPN or the Internet.
⚡ SD-WAN Vs. Legacy Networks 🎪
The single hub and spoke topology is a popular representation of the legacy WAN solution. The user experience on cloud-native apps may suffer significantly as a result of branch traffic travelling to headquarters for administration or security purposes in this typical WAN architecture.
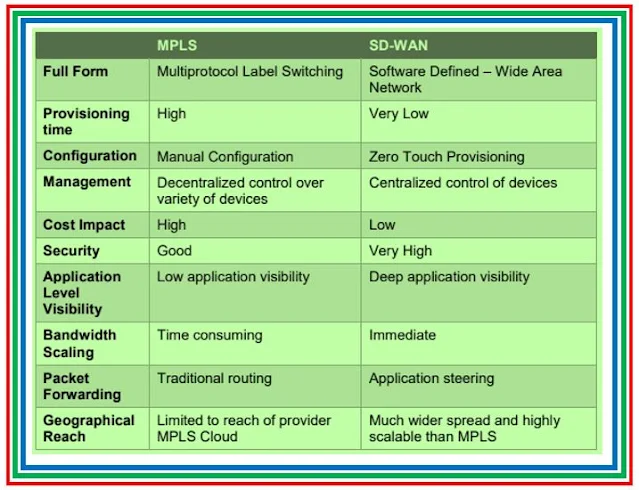 |
| Fig 1.2- MPLS Vs. SDWAN |
⚡ SDWAN Design Consideration ⭐⭐
- Cost Savings : For the transfer of business data between headquarters and branches, many organizations require a high bandwidth connection. The SD-WAN may be deployed in a flexible manner using DSL, cable, Ethernet, wireless, and other internet connection methods.
- Improving reliability : By working with different IPS, organizations may contract for a variety of WAN connections, each of which offers traffic control and application steering to improve branch dependability.
- Traffic identification: When connecting to a central data center or headquarters, the hub-and-spoke WAN design introduces backhaul problems. A lot of businesses are implementing direct point-to-point connections between branches and the Internet for cloud or SaaS application access. By using user-driven rules, SD-WAN can guarantee business-critical apps.
- Fast deployment : With zero touch provisioning, branches may be set up quickly and easily for organizations. Usually, the SDWAN hardware device is delivered to the branch, connected to the WAN and AC power sources, and configured remotely via the cloud.
- Multi-cloud access : Many businesses require access to both SaaS applications and internal data centers as well as applications hosted in public clouds. Because SD-WAN solutions offer the closest point of presence (PoP), traffic to the cloud may be expedited.
⚡ Comparing SDN vs SD-WAN 📜
These days, SDN and SD-WAN are transforming the conventional network design. When it comes to the ability to directly programme network control through the decoupling of forwarding and network control operations, these two most recent technologies are rather comparable in several respects.
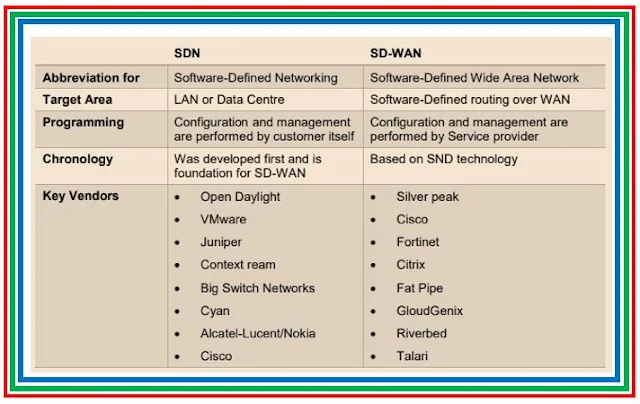 |
| Fig 1.2- SDN Vs. SDWAN |
⚡ SD-WAN Security 🔐
SD-WAN has incorporated IPsec, next-generation firewalls, and micro-segmentation of application traffic to provide the security of user traffic from internet threats, as the communication between the branch and headquarters is carried via the Internet.
- IPSEC VPNs : By encrypting traffic, IPsec-based VPNs offer secure connections and guarantee data integrity for enterprises.
- SSL Inspection: Hidden malware in encrypted traffic poses a significant risk to organizations. Using SSL inspection as part of an SD-WAN solution is an efficient way to detect and eradicate this sort of attack.
⚡ Firewall & SDWAN 🔐
- SDWAN Secure options: While the network is being continuously monitored and protected thanks to the integration of a next-generation firewall (NGFW), this design also makes daily management tasks and network deployment easier.
- SDWAN with 3rd Party Firewalls: One way to enhance the security of an SD-WAN network is to implement NGFW at both headquarters and branches. With the use of application awareness, next-generation instruction detection and prevention, Web filtering, malware detection, antivirus, and sandbox, NGFW gives enterprises the capacity to defend against both known and undiscovered threats. Organizations are starting to take the cloud-base deployment into consideration more often.
Continue Reading...
- MPLS Vs VPLS : Difference & Design - The Network DNA
- What to choose L2MPLS or L3MPLS - The Network DNA
- MPLS Constraint-based Routing Label Distribution Protocol- (CR-LDP)
- MPLS ( RD and VRF concept ) - The Network DNA
- Part 4: MPLS Forwarding Operations (LDP Vs RSVP)
- Ethernet Over MPLS -EoMPLS
- ICMP trace-route in MPLS network
Free Tools...







