MTU vs. MSS: What Every Network Administrator Should Know
MTU vs. MSS: What Every Network Administrator Should Know
In order for a data packet or block to be able to be transmitted via a computer network as a single, uninterrupted unit, its size must be determined. Two crucial components of computer networking are MSS and MTU. Maximum TCP Segment Size, or MSS, employs three-way handshaking to meet all the requirements of fundamental networking protocols.
The maximum transmission unit, or MTU, determines a host computer's capacity to send and receive big data blocks and files simultaneously at a specific time over a computer network. The safer and more sophisticated variant of MTU is called MSS.
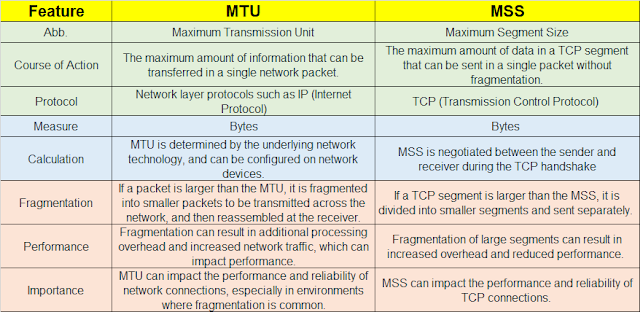
 |
| Fig 1.1- MTU Vs. MSS |
⭐ MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit)
The maximum size of a data packet that an internet-connected device will allow is indicated by the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) measurement. It restricts the size of data packets for all networked devices and is often expressed in bytes. Packets and IP fragmentation are impacted by MTU network parameters.
It stands for the biggest frame or packet size that can be delivered across network interfaces without becoming fragmented.
MTU size is essential for effective data transmission because higher packet sizes may necessitate fragmentation, which could create performance problems, while smaller packet sizes may result in more overhead from extra headers.
MTU sizes vary throughout different network technologies and protocols. For example, the maximum transmission unit (MTU) of Ethernet is usually 1500 bytes, while alternative technologies, such as PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet), may have a lower MTU.
- Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size of IP packets that are sent on an interface. If the df-bit [don't fragment] is set, then the packets exceeding the MTU size would be dropped
- IP MTU operates at Layer 3
- To set ip mtu, use the "ip mtu" command in interface configuration mode as shown below. The following example shows how to set the maximum IP packet size on a serial interface to 300 bytes:
NDNA(config)# interface serial 0
NDNA(config-if)# ip mtu 300 - If an IP packet exceeds the MTU size that is set for the interface, the Cisco software fragments the IP packet.
⭐ MSS (Maximum Segment Size)
The maximum amount of data from the TCP segment payload that can be transferred in a single segment or packet across a TCP/IP network is referred to as MSS. It is a TCP-specific parameter that is negotiated between two devices during the formation of a TCP connection.
MSS eliminates the TCP header and IP header sizes from the overall packet size. It represents the most data that can be provided within a TCP segment without imposing IP layer fragmentation.
The minimum of the MTU values of the two endpoints along the path is commonly used to calculate MSS size. The MSS value is agreed upon during the TCP handshake (the procedure of connection initiation) depending on the smallest MTU in the network path to enable effective data delivery without fragmentation.
- Adjusts the maximum segment size (MSS) value of TCP synchronize/start (SYN) packets that go through a router
- When a host (usually a PC) initiates a TCP session with a server, the host negotiates the IP segment size by using the MSS option field in the TCP SYN packet. The value of the MSS field is determined by the maximum transmission unit (MTU) configuration on the host. The default MSS size is 1460 bytes, when the default MTU of the containing IP datagram is 1500 bytes.
- The "ip tcp adjust-mss" command helps prevent TCP sessions from being dropped by adjusting the MSS value of the TCP SYN packets
- The "ip tcp adjust-mss" command is effective only for TCP connections that pass through the router. The following example shows how to set ip tcp mss on an interface
NDNA(config)#interface ethernet0/1
NDNA(config)#ip tcp mss 1460 - TCP MSS operates at Layer 4. It is 40 bytes lower than the IP MTU as it does not take headers into consideration (20 byte IP header and 20 byte TCP header).
- When applied to a router's interface, the router will monitor this interface's incoming and outgoing traffic, looking for SYN packets (which is where hosts define their MSS).
⭐ MTU Vs. MSS
MTU and MSS are essential for enhancing network performance, reducing fragmentation, and assuring data transmission efficiency. While MTU refers to the total packet size at the network layer, MSS is concerned with the payload size at the transport layer for TCP.
⭐Related : All about IP MTU and IP TCP MSS - The Network DNA
Continue Reading...
- 51 facts about BGP routing Protocol for Network Engineers
- BGP Conditional Advertisement Feature
- BGP: Path Selection Criteria - Path Vector Protocol
- Understanding BGP ORF: An Essential Guide
- 2023: BGP AS Override vs BGP Allow-AS-In: A Comprehensive Comparison
- BGP Next Hop Unchanged: Solving Common Routing Challenges
- BGP Protocol : iBGP vs MP-iBGP protocol - The Network DNA
- BGP : bgp deterministic-med and bgp always-compare-med
- BGP Basics: BGP Neighbor States
- BGP Attribute : AIGP-BGP Accumulative IGP