Understanding BGP ORF: An Essential Guide
Understanding BGP ORF: An Essential Guide
The outbound route filter is filtered using BGP ORF. This functionality is being developed to keep outgoing and incoming bgp updates brief in order to reduce CPU and device utilization.
It is a feature that leverages BGP outbound route filter (ORF) transmit and receive capabilities to reduce the amount of BGP updates delivered between BGP peers. By filtering out undesirable routing updates at the source, you may assist decrease the amount of system resources required for creating and processing routing updates.
 |
| Fig 1.1- BGP ORF Topology |
One of the CE routers in your network is linked to the PE router of the service provider and establishes an EBGP neighborship with it. The CE router only wants to receive a set amount of prefixes from PE in addition to the default route; otherwise, it would process the entire set of routes and burn up CPU resources. In order to do this, you will consider two possibilities.
⭐ Possibility No 1 👇
Set the PE's output filter to block prefixes that CE does not want. This will work, but there is a catch: you will have to create a service request with the service provider and wait for them to finish if your CE needs more specialized routes in the future for whatever reason, such as path manipulation. Additionally, this will make it more difficult for service provider engineers to manually add, remove, or alter the filter list.
⭐ Possibility No 2👇
To obtain the necessary prefixes for the routing table and to filter out undesired data arriving from PE, configure the incoming filter list on CE. This will function flawlessly; the customer in charge of the CE router will be able to decide which prefixes to keep and which to discard. Reduce the SP engineer's configuration portion as well.
Everything is OK, however if you look closely, you'll see that there is one problem with the design. Imagine what would happen if your CE received high routes like 1000 routes.
Even with an incoming filter list configured on CE, PE is still advertising all chunk routes to CE. CE must then search for every prefix arriving from PE and filter them according to setup.
In this case, the BGP ORF capability feature may be important. When you set up BGP ORF, PE routers will dynamically learn the filter-list of CE routers, and PE will only broadcast the prefixes that CE routers require.
⭐Related : BGP: Path Selection Criteria - Path Vector Protocol
⭐ Configuration check & Setup📜
Prior to configure anything, we must make sure that all of the BGP components are appropriately installed and operational on both sides.
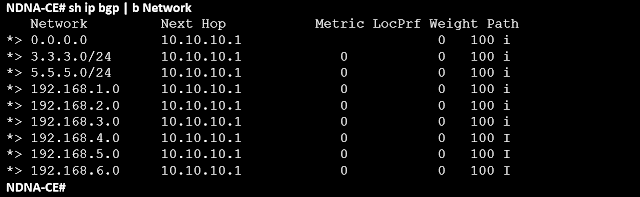
Observe that CE has picked up 9 routes from PE.
The default route and the 3.3.3.0/24 and 5.5.5.0/24 subnets are all that the CE site engineer wants for now; no further subnets are desired.
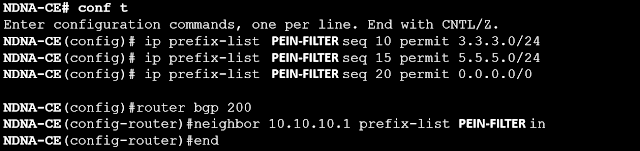
As was previously said, there are two methods to set a filter list: either inbound to CE or outward to PE. We also spoke about potential issues. As a result, we are setting up a filter list for incoming traffic to CE.
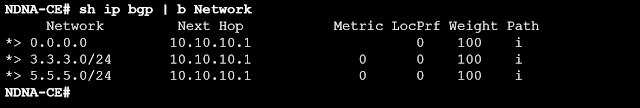
Now, after using the filter-list, check the BGP table.
The BGP table shows that only three prefixes are required after applying the filter-list, however as was previously said, PE sends the complete BGP table to CE.
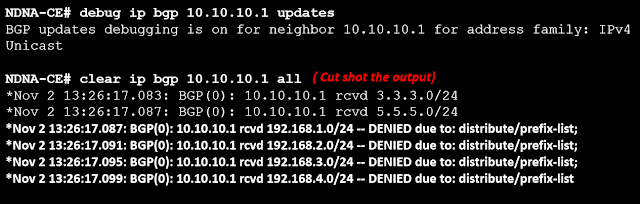
As a result, CE must analyze all BGP updates from PE before filtering according to the specified list, which might waste CE CPU. Let's troubleshoot and clear BGP updates.
The command "sh ip bgp neighbors 10.10.10.1 received-routes" can also be used to confirm this.
Its time to apply BGP ORF now and then will see
The BGP ORF only supports prefix-list filtering, not route-map or any other filtering technique. This may be enabled on a router to transmit or receive ORF capabilities using either the send or receive keywords.
With the both keyword, this functionality may be set on a router to send and receive ORF capabilities.
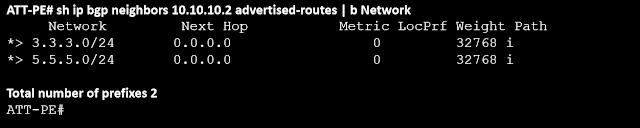
On the AT&T PE side, lets check the advertised routes to verify
We can see from the output above that the CE router was previously receiving updates from the PE router, which was sending the whole BGP table to it.
The CE router dynamically informs the PE router which routes to filter as "outbound" while using BGP ORF. As a result, only update messages regarding the prefixes that the CE router desires will reach it.
Continue Reading...
- Why BGP-SRx is a Must-Have for Large Enterprises
- 51 facts about BGP routing Protocol for Network Engineers
- BGP Conditional Advertisement Feature
- Quick facts on BGP for interviews
- BGP Protocol : iBGP vs MP-iBGP protocol
- BGP : bgp deterministic-med and bgp always-compare-med
- BGP Attribute : AIGP-BGP Accumulative IGP
More on BGP...