Introduction to FortiGate SDWAN Zones
Introduction to FortiGate SDWAN Zones
Businesses need a comprehensive SD-WAN solution like Fortinet Secure SD-WAN to meet these business requirements, the only one that is both secure and flexible for deployment across any size organization.
Rather than separately controlling WAN routers, WAN optimization, and security devices like firewalls and secure web gateways (SWGs), FortiGate Secure SD-WAN integrates these into a single FortiGate NGFW.
By advancing efficiency without compromising security, FortiGate provides next-generation security and networking capabilities. With Fortinet SDWAN, you can provide visibility and prevention against malware with SSL inspection and threat protection.
With Web filtering, internet security can be enforced and complexity is reduced, eliminating the need for separate SWG devices. The SDWAN solution offered by Fortinet is highly scalable, and IPsec VPN tunnels can be established to ensure that traffic is always encrypted and confidential.
 |
| Fig 1.1- Introduction to FortiGate SDWAN Zones |
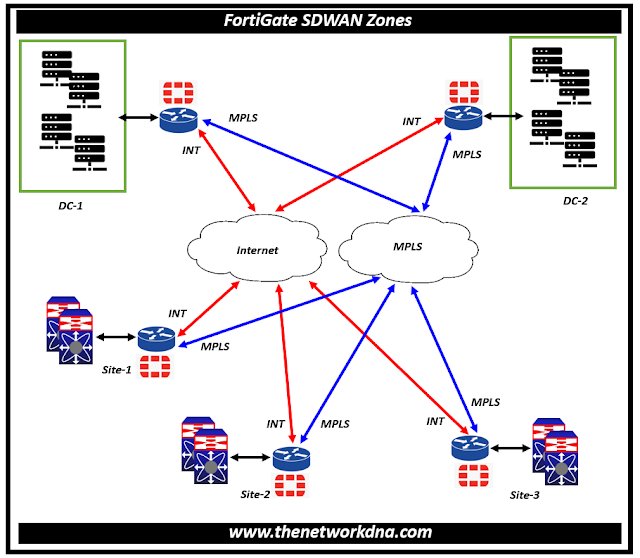
FortiGate SDWAN Zones basics
To assign policies, static routes, and SD-WAN rules, SD-WAN members are logically grouped into zones. Multiple zones can be used to group SD-WAN interfaces together. Firewall policies, source and destination interfaces use SD-WAN zones.
They offer more precise network control. Policies cannot be directly allocated to SD-WAN members. It is not possible to share SD-WAN members within different SD-WAN zones.
For logical circumstances like overlay and underlay interfaces, multiple zones can be used to set up SD-WAN interfaces. Further control over features like UTM access and resource access is possible with the use of different zones in policies.
Although they cannot be used directly in policies, individual SD-WAN member interfaces can be relocated at any moment across SD-WAN zones. A member interface may be placed in an SD-WAN zone by itself if it needs special SD-WAN consideration.
FortiGate SDWAN Zones Configuration
Although the main function of SD-WAN zones is to logically combine interfaces that are frequently used for the same purpose (like INT and MPLS), an SD-WAN zone may occasionally have just one member. The reason for this is that while SD-WAN members can be directly addressed in SD-WAN rules, they cannot be directly mentioned in policies.
To configure the SD-WAN zones in the GUI:
- Step 1: Go to Network > SD-WAN and select the SD-WAN Zones tab.
- Step 2: Click Create New > SD-WAN Zone.
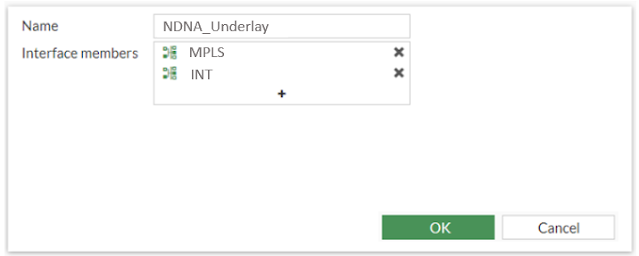
- Step 3: Enter the Name, NDNA_Underlay.
- Step 4: Set the Interface members to INT and MPLS. Click OK.
- Step 5: Repeat these steps to configure the Overlay zone with members VPN1 and VPN2.
To configure the SD-WAN zones in the CLI:
1. Configure the SD-WAN zones:
2. Add the member interfaces to their respective zones: