Frame Tagging : ISL vs IEEE 802.1Q
Frame Tagging : ISL vs IEEE 802.1Q
At layer 2, broadcast domain is divided using VLANs. Every switch port is automatically assigned to VLAN 1. If you configure VLANs other than VLAN 1, you will need to create a switch port trunk that is connected to another switch in order to transport traffic from those VLANs.
The frame will be considered as corresponding to the VLAN that is configured on that switch port if it is sent to an access connection. However a header or tag identifying the VLAN to which the frame belongs is added to the frame header if the frame is sent to a trunk link.
According to the switch's processing, the frame is encapsulated at the sender's switch, removed at the receiver's switch, and then forwarded to the ports that are part of that VLAN.
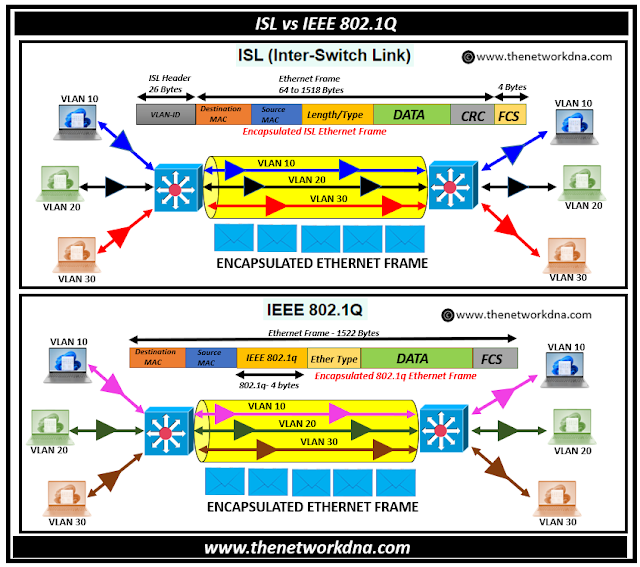
Fig 1.1- Frame Tagging : ISL vs IEEE 802.1Q
⭐Related : CCNA RnS #11: Ethernet/MAC Addressing
⭐Related : CCNA RnS Article #25: Inter-VLAN Routing
What is ISL (Inter-Switch Link) ?
Cisco created the proprietary VLAN protocol known as Inter-Switch Link (ISL) with the goal of facilitating communication between Cisco switches. Using explicit VLAN tagging on an Ethernet frame, ISL is a technique for VLAN identification.
In order to conduct ISL operations at layer 2, a new cyclic redundancy check (CRC) and a new header are applied to a data frame. To transfer a frame across a trunk connection in ISL, the original frame is encapsulated and a new header is added.
Once the header is extracted, the frame is routed to the designated VLAN at the receiving end. ISL does not need to understand native VLAN because all frames, including those for native VLAN, are tagged.
Features of ISL (Inter-Switch Link)
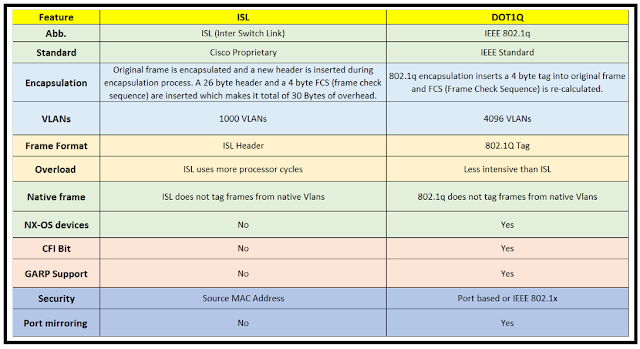
- Standard: ISL is a proprietary VLAN tagging protocol developed by Cisco, and is only supported on Cisco devices.
- Adds a 26-byte header: ISL encapsulates the entire Ethernet frame, adding a 26-byte header and a 4-byte trailer to the original frame. This includes VLAN information along with other control information.
- Overhead: ISL encapsulates the entire Ethernet frame, resulting in additional overhead, which can slightly reduce the available bandwidth for user data.
- Compatibility: ISL is proprietary to Cisco and is primarily supported on Cisco's networking devices. It may not be compatible with devices from other vendors.
- Supports up to 1,005 VLANs: ISL supports up to 1,005 VLANs, which can be useful in large network environments.
- Security: ISL does not provide the same level of security as Dot1q, as VLAN information is encapsulated within the frame, making it potentially vulnerable to certain attacks.
What is IEEE 802.1Q ?
IEEE 802.1Q is an open standard that can be used to tag frames on trunk lines in networks made up of different kinds of Ethernet switches or routers.
To enable trunking between a Cisco switch link and a switch link from a different brand, the user must use 802.1Q encapsulation.
Before sending a frame via the trunk connection in 802.1Q, the trunking device calculates the frame check sequence (FCS) and inserts a 4-byte tag into the original frame. The frame is sent to the desired VLAN at the receiving end after the tag is removed.
⭐Related : CCNA RnS Article #27: VLAN Trunking Configuration
Features of IEEE 802.1Q
- Industry-standard protocol: IEEE 802.1Q is an industry-standard VLAN tagging protocol supported by most network devices.
- Adds a 4-byte tag: IEEE 802.1Q adds a 4-byte VLAN tag to the Ethernet frame header, which includes VLAN information such as VLAN ID (VID) and priority information
- Supports up to 4,096 VLANs: IEEE 802.1Q supports up to 4,096 VLANs, which can be useful in large network environments.
- Overhead: Dot1q is considered more efficient in terms of bandwidth usage because it only adds a small tag to the frame header, rather than encapsulating the entire frame like ISL
ISL Vs. IEEE 802.1Q
Virtual LANs (VLANs) on an Ethernet network are supported by two encapsulation standards: ISL and DOT1Q. The two frame tagging protocols differs as:
Hope now you understand the difference between ISL vs IEEE 802.1Q in detail. Well now a days almost all organizations used IEEE 802.1Q with the better security, less intensive and useful.
- Why BGP-SRx is a Must-Have for Large Enterprises
- 51 facts about BGP routing Protocol for Network Engineers
- BGP Conditional Advertisement Feature
- Quick facts on BGP for interviews
- BGP Protocol : iBGP vs MP-iBGP protocol
- BGP : bgp deterministic-med and bgp always-compare-med
- BGP Attribute : AIGP-BGP Accumulative IGP