Introduction to RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In Service)
Introduction to RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In Service)
The RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In Service) protocol is a client-server networking protocol that allows a central server to communicate with individual users requesting access to the server.
Essentially, RADIUS enables remote access servers to interact with the central server in order to authenticate and authorize distant user access. RADIUS allows businesses to maintain user profiles in a central database that can be shared by all distant servers.
How RADIUS Works ?
RADIUS is built on the client/server architecture. Users connect to a network access server (NAS), often known as a RADIUS client. The NAS then checks the user's details using the RADIUS authentication server. The connection information may comprise a login, password, and IP address.
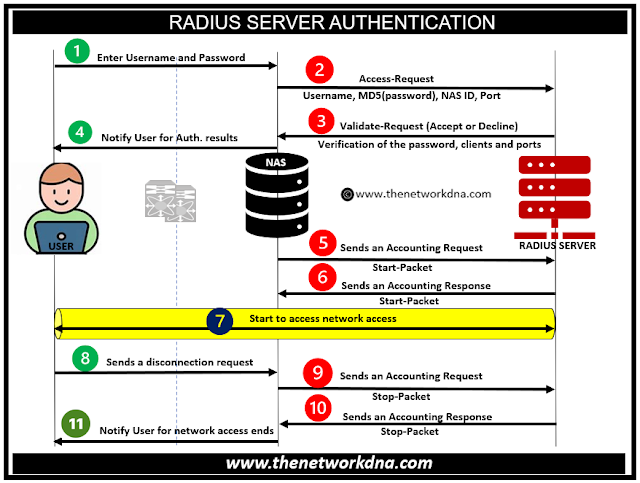 |
| Fig 1.1- Introduction to RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In Service) |
What is the main purpose of RADIUS servers ?
Well the major purpose of the RADIUS server in the network is described as below.
- Authenticates users or devices before allowing them access to a network
- Authorizes those users or devices for specific network services
- Accounts for and tracks the usage of those services
RADIUS Authentication methods
After a user enters their login credentials, the RADIUS server employs one of the following authentication techniques:
- Password Authentication Protocol (PAP): A RADIUS client sends a user ID and password to the RADIUS authentication server. If the credentials are correct, the client permits the remote user to connect.
- Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP): The client and server exchange an encrypted secret. It is regarded more secure than PAP.
- MS-CHAP is Microsoft's version of CHAP. It is used with virtual private networks.
- Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP): This protocol is commonly used for wireless networks and point-to-point connections.
Architecture and advantages of RADIUS server
- The Battle of the Data Transports: Ethernet vs MPLS
- Decoding VRF Vs VRF Lite
- MPLS LDP Basic Concepts
- MPLS LDP Loop Detection
- TTL Processing in MPLS
- Basics: How to configure MPLS and MPLS Traffic Engineering
- Do you know about VRF lite in MPLS networks ?
- Introduction to VRF(Virtual Routing forwarding)
- Part 4: MPLS Forwarding Operations (LDP Vs RSVP)
- A brief about MPLS Header & Label







