Understanding EVPN Data Plane: The Basics
Understanding EVPN Data Plane: The Basics
💻 Table Of Content
- What is EVPN?
- Discover the Benefits of EVPN Compared to VPLS
- EVPN Data Plane
- EVPN-MPLS Data Plane
- EVPN- Provider Backbone Bridge (PBB) Data Plane
- EVPN- Network Virtualization Overlay Data Plane
What is EVPN?
EVPN (Ethernet Virtual Private Network), enables virtualized Ethernet communication between various network devices. Data center and service provider networks frequently employ EVPN to offer effective and scalable network connection.
EVPN provides several benefits over traditional Layer 2 VPN technologies, such as Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS). One of the main benefits of EVPN is that it enables multi-tenancy, where multiple customers or tenants can share the same physical infrastructure while maintaining separate and secure virtual networks.
EVPN also provides more efficient use of network resources and better scalability compared to traditional Layer 2 VPN technologies.
Discover the Benefits of EVPN Compared to VPLS
Are you considering switching to an EVPN from VPLS for your network? Read on to learn about the advantages that EVPN offers over VPLS.
Scalability
EVPN provides better scalability than VPLS, especially for large-scale networks with many customers or tenants. It uses Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to distribute routes, which helps conserve network resources and makes the forwarding plane less complex.
Multi-tenancy
EVPN allows multiple customers or tenants to share the same physical infrastructure while keeping their virtual networks separate and secure. This is especially useful for service providers who need to provide multiple customers with different network needs.
Control Plane Separation
With EVPN, the control plane is separated from the data plane, which makes network designs more flexible and troubleshooting easier. This is in contrast to VPLS, where the control and data planes are linked together.
MAC Address Learning
EVPN provides an improved MAC address learning process, especially for networks with many customers or tenants. This is because it uses BGP to distribute MAC addresses, which reduces the amount of flooding and enhances the efficiency of the forwarding plane.
Support for Layer 3 Services
EVPN supports Layer 3 services, such as IP VPNs and MPLS VPNs, in addition to Layer 2 services. This makes it easier for service providers to offer a wider variety of services to their customers.
EVPN Data Plane
EVPN abstracts and separates the control plane and the data plane. Multiprotocol BGP as the control plane with different data plane encapsulation choices can be below- EVPN-MPLS Data Plane
- Provider Backbone Bridge (PBB)
- Network Virtualization Overlay
EVPN-MPLS Data Plane
In today's competitive business landscape, having a reliable and secure way to connect with customers and partners is essential. That's why more and more companies are turning to EVPN-MPLS. This data plane is responsible for the delivery of Layer 2 services over an MPLS backbone. It's based on the concept of a Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN), which provides a virtual private network for Ethernet traffic over an MPLS core.
 |
| Fig 1.1-EVPN MPLS Data Plane |
It offers a secure connection that can be quickly provisioned and scaled to accommodate the needs of your growing business. Plus, its high availability architecture ensures that your data is always accessible, even during peak periods of traffic.
- EVPN-MPLS Data plane is the original EVPN solution in the base specification, it provides a simple method of implementing EVPN over an existing MPLS core.
- MPLS runs in the core networks control plane and data plane providing all the MPLS features.
- Provides all active multihoming for Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS).
- It requires no PseudoWires.
- IGP, RSVP-TE or LDP is required for MPLS and BGP for EVPN
EVPN- Provider Backbone Bridge (PBB) Data Plane
EVPN-PBB is an innovative technology combining IEEE 802.1ah PBB with EVPN to help networks scale up to unprecedented levels, with all active multihoming over MPLS. By aggregating customer MAC addresses with backbone MACs, the same concept of route aggregation used in IP, EVPN-PBB significantly reduces the number of MAC addresses needed to keep a network running.
 |
| Fig 1.2-Provider Backbone Bridge (PBB) – EVPN Data Plane |
Backbone Edge Bridges (BEB) PEs only advertise backbone MACs using BGP, while the customer MAC and backbone MAC mapping is learned in the data plane. MPLS runs in both the control plane and the data plane, making EVPN-PBB an architecture that can make a huge difference in large networks with high MAC scalability requirements.
- Put simply, EVPN-PBB can take your network to the next level. By making use of this powerful technology, you can unlock scalability on a scale you never thought possible.
- PBB-EVPN combines IEEE 802.1ah PBB with EVPN to support scaling of very large networks with all active multihoming over MPLS.
- It lowers the number of MAC addresses by aggregrating customer MACs with backbone MACs, same concept as of route aggregation in IP.
- Backbone Edge Bridges (BEB) PEs only advertise backbone MACs with BGP, while customer MAC and backbone MAC mapping is learned in the data plane.
- MPLS runs in the control plane and the data plane. This architecture can be useful where the number of MAC addresses are too large as this hides the customer MACs from the backbone elevating to high MAC scalability.
EVPN- Network Virtualization Overlay Data Plane
Are you looking to leverage the power of EVPN over NVO tunnels (VXLAN,NVGRE,MPLSoGRE) to provide L2 and L3 Data Center Interconnect and resilience to simple IP networks? If yes, then EVPN-VXLAN Data Plane is your answer!
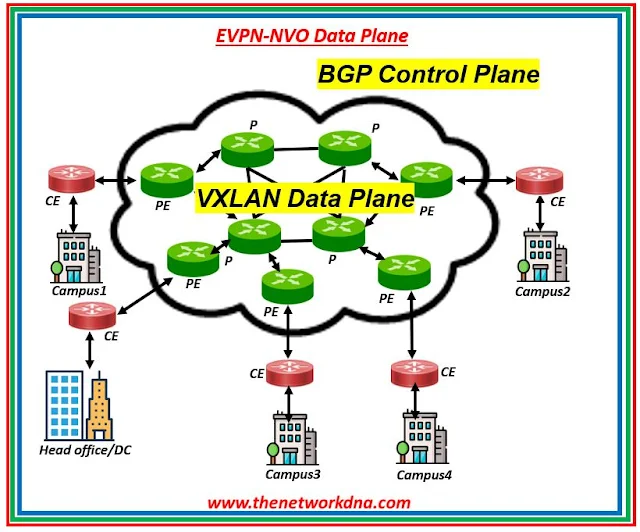 |
| Fig 1.3- EVPN-NVO Data Plane |
Unlike MPLS Data plane, EVPN-VXLAN Data Plane can be used to provide an L2 overlay over an IP network. It is quite flexible, VXLAN can be routable with IP irrespective of the underlying network being used. This architecture can provide EVPN services to DCI and virtual network without requiring MPLS.
- EVPN over NVO tunnels (VXLAN,NVGRE,MPLSoGRE) provides L2 and L3 Data Center Interconnect and resilience to simple IP networks.
- EVPN over Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) Data Plane can be used in place of MPLS Data plane when MPLS is not available in the core network
- EVPN-VXLAN can be used to provide an L2 overlay over an IP network. It is quite flexible, VXLAN can be routable with IP irrespective of the underlying network being used.
- VXLAN Data plane encapsulates VXLAN header and L2 Frame using UDP and can run over IPv4 or IPv6 while EVPN uses BGP Control Plane to advertise MAC routes.
- Possible to provide a VPN to a hypervisor attached to a Virtual Machine, as the VXLAN tunnel endpoints can be on Virtual Machines.
- This architecture can provide EVPN services to DCI and virtual network without requiring MPLS.







