Decoding SNAT and DNAT: Unveiling the Variances
Decoding SNAT and DNAT: Unveiling the Variances
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a service that allows private IP networks to connect to the internet and the cloud. Before packets are delivered to an external network, Network Address Translation (NAT) converts private IP addresses in an internal network to public IP addresses.
⭐ NAT Advantages 👇
- Network Address Translation (NAT) helps to mitigate the depletion of the global public IP address space
- Networks can now use the RFC 1918 private address space internally and still have a way to access the Internet using Network Address Translation (NAT).
- Network Address Translation (NAT) increases security by hiding the internal network topology and addressing scheme.
Lets talk about SNAT and DNAT with the comparison between them.
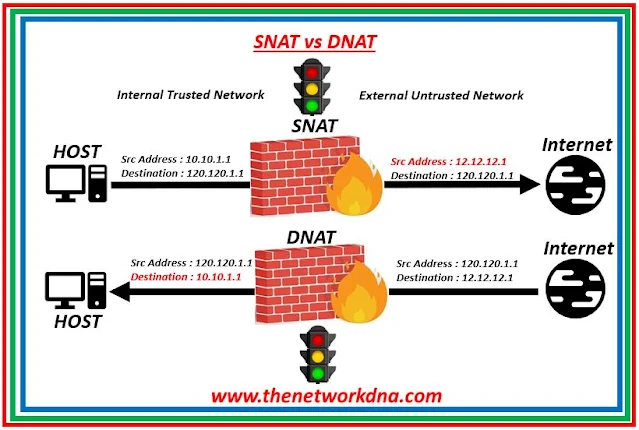 |
| Fig 1.1- SNAT vs DNAT |
⭐ Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) 👇
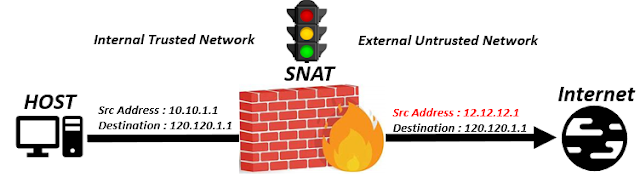
By utilizing a public IP address and port, devices connected to a private network can access the internet through the use of Source Network Address Translation (SNAT). Below is the scenario defining SNAT where you see the source IP changes from 10.10.1.1 to 12.12.12.1 to save the internal private IP from the external untrusted networkFig 1.2- SNAT
With SNAT, a load balancer, Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway, or router, or any other device that does SNAT, modifies the source IP address and port of outgoing packets to match its public IP address and port. SNAT enhances security by obscuring the devices' private IP addresses, which helps preserve public IP addresses.
⭐ Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) 👇
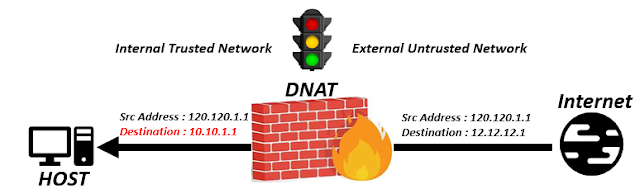
DNAT is a technology that allows devices on the public network to access devices or services on the private network by utilizing a public IP address and port. DNAT modifies the destination IP address and port of incoming packets to match the private IP address and port of the DNAT device or service, which might be a firewall, Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway, or router.
By masking the private IP addresses of devices or services behind DNAT, DNAT helps to conserve public IP addresses while also improving security.Fig 1.3- DNAT
Above is the scenario defining DNAT where you see the destination IP changes from 12.12.12.1 to 10.10.1.1 as described earlier.
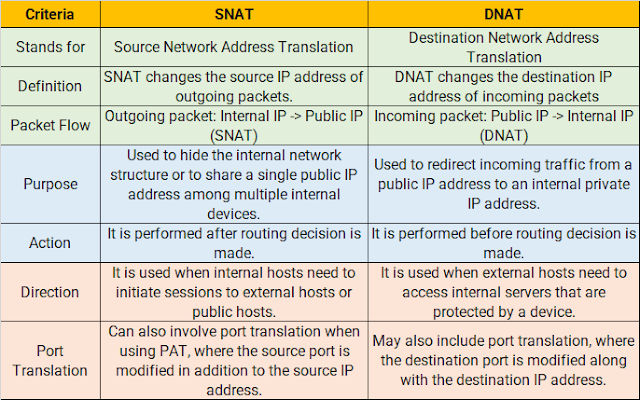
⭐ SNAT vs DNAT 👇
Here is a table that compares SNAT (Source Network Address Translation) and DNAT (Destination Network Address Translation)
To summaries, SNAT is concerned with altering the source IP address of outgoing packets, whereas DNAT is concerned with changing the destination IP address of arriving packets. SNAT is used to give internet access, whereas DNAT is utilized to host services and route incoming traffic.
Continue Reading...
- Introduction to the NAT, PAT, Dynamic NAT and Static NAT
- A brief about PAT- Port Address Translation
- NAT Overloading akka PAT inside global addresses
- Cisco Viptela SDWAN: NAT Mapping and Filtering Test
- Server Load Balancing Using Dynamic NAT Configurations
- Carrier Grade NAT (CGNAT) and BIG-IP CGNAT
- Configure NAT to Enable Communication Between Overlapping Networks