NAT & DHCP Services on VMware NSX-T
Today we are going to discuss about the NAT and DHCP services on the VMware NSX-T 2.5. Users can enable NAT as a network service on NSX-T. This is a centralized service which can be enabled on both Tier-0 and Tier-1 gateways.
NAT Services on VMware NSX-T
Remember earlier we discuss about the Tier-0 and Tier-1 gateways and the supported NAT rules are Source NAT (SNAT); Destination NAT (DNAT) and Reflexive NAT. Let's discuss all these three types of NAT one by one supported in the VMware NSX-T environment.
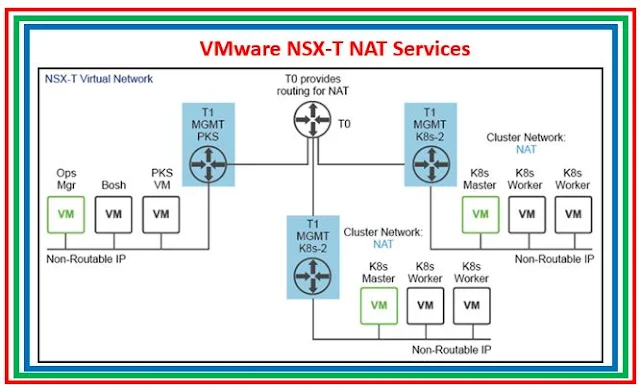 |
| Fig 1.1- NAT services on NSX-T |
Source NAT (SNAT):
Source NAT translates the source IP of the outbound packets to a known public IP address so that the application can communicate with the outside world without using its private IP address. It also keeps track of the reply.
Destination NAT (DNAT):
DNAT allows for access to internal private IP addresses from the outside world by translating the destination IP address when inbound communication is initiated. It also takes care of the reply. For both SNAT and DNAT, users can apply NAT rules based on 5 tuple match criteria.
Reflexive NAT:
Reflexive NAT rules are stateless ACLs which must be defined in both directions. These do not keep track of the connection. Reflexive NAT rules can be used in cases where stateful NAT cannot be used due to asymmetric paths (e.g., user needs to enable NAT on active/active ECMP routers).
 |
| Fig 1.2- NAT Rules |
DHCP Services on VMware NSX-T
NSX-T provides both DHCP relay and DHCP server functionality. DHCP relay can be enabled at the gateway level and can act as relay between non-NSX managed environment and DHCP servers.
DHCP server functionality can be enabled to service DHCP requests from VMs connected to NSX-managed segments.
DHCP server functionality is a stateful service and must be bound to an Edge cluster or a specific pair of Edge nodes as with NAT functionality.







