Comparing Router Vs. Layer 3 Switches
Comparing Router Vs. Layer 3 Switches
This is a common discussion over why we need a switch at Layer 3 if there is a router. What precisely distinguishes a Layer 3 switch from a router?
Routers are commonly used for routing across networks or when more complex routing functions are required, whereas Layer 3 switches are commonly used for routing inside a subnet or VLAN.
⭐Related : Are you a starter in Networking : OSI model
⭐Related : OSI model vs TCP/IP model
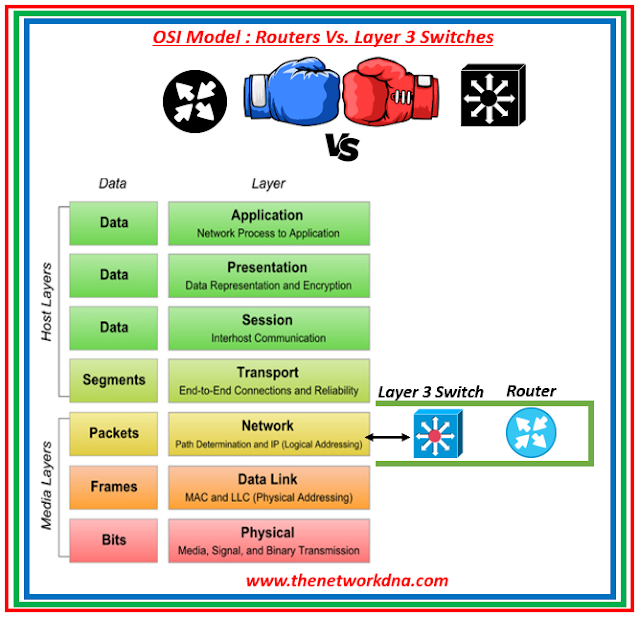 |
| Fig 1.1-Router Vs. Layer 3 Switch |
⭐ Routers 🔄
A router is a network device that links and routes data traffic between inter VLAN networks. It works at the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model's third tier, known as the Network tier or Layer 3. Routers, by making decisions based on IP addresses, play an important role in allowing communication between devices on various subnets or networks.
A router uses an internal routing table, which is a collection of pathways to different network destinations, to efficiently route packets. After identifying the destination of a packet by reading its header, the router uses the routing table to calculate the fastest route to that location. The packet is subsequently sent to the following network along the route.
⭐ Layer 3 Switches 🔄
A layer 3 switch, also known as a multilayer switch, may perform all of the functions of a layer 2 switch as well as extra static and dynamic routing. That is, a Layer 3 switch contains a MAC address table as well as an IP routing table and supports intra-VLAN communication as well as packet routing between VLANs.
Layer 3 switches, in addition to routing packets, provide functionalities that involve understanding the IP address information of data entering the switch, such as tagging VLAN traffic based on IP address rather than manually establishing a port. Layer 3 switches' power and security are upgraded as needed.
Each port on a Layer 3 switch can be treated as its own broadcast domain, decreasing the impact of broadcast storms on network performance and boosting network security.
Layer 3 switches can support a variety of routing protocols (including RIP, OSPF, BGP, and others) to enable dynamic routing updates and choices with other routers or layer 3 switches, boosting network dependability and flexibility.
Layer 3 switches can offer policy routing depending on source IP address, destination IP address, protocol type, and other criteria, allowing for varied processing or forwarding of data packets of varying sorts or priorities and thereby enhancing network efficiency and quality.
⭐Related : Layer 2 vs. Layer 3 Switches: Which One Is Right for Your Network?
⭐ Router Vs. Layer 3 Switches 🔄
As you read above both these devices are act on layer 3 of OSI model helping routing over the inter-VLAN networks, but still the question when to use what, so here is the difference to make decision what device you should use on the basis of below analysis
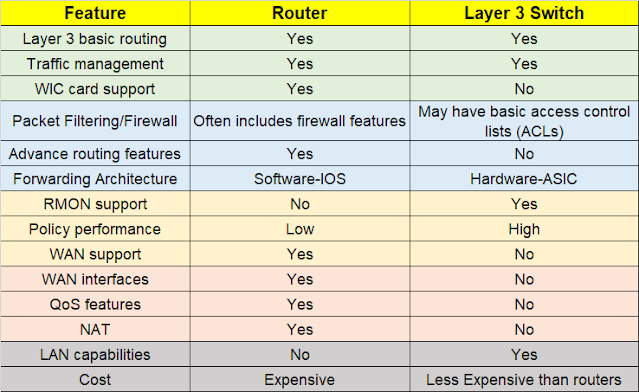 |
| Fig 1.2- Router Vs. Layer 3 Switch |
Prior to selecting between a layer 3 switch and a router, you must ascertain the following business requirements: Generally speaking, it makes sense to purchase a router if your device handles routing the majority of the time; otherwise, a layer 3 switch would be more appropriate if you want additional ports, improved network speed, and VLAN segmentation.
⭐Related : CCNA RnS #16: Campus vs Data Center Network
- CCNA RnS Article #36: Improve STP with EtherChannel (L2 Static)
- CCNA RnS Article #35: Make STP Better & Secure
- CCNA RnS Article #33: How STP & RSTP Relate?
- CCNA RnS Article #32: Influencing STP
- CCNA RnS Article #31: STP Behavior
- CCNA RnS Article #30: STP: Under the Hood
- CCNA RnS Article #29: What STP Does?
- CCNA RnS Article #28: Why Spanning Tree Protocol?
- CCNA RnS Article #27: VLAN Trunking Configuration
- CCNA RnS Article #26: Configuring VLANs
- CCNA RnS Article #25: Inter-VLAN Routing
- CCNA RnS Article #24: VLAN Tagging






